NVIDIA Corporation announced that the LLVM open source compiler now supports NVIDIA’s Graphics Processing Units (GPUs).
NVIDIA Corporation announced that the LLVM open source compiler now supports NVIDIA’s Graphics Processing Units (GPUs).
For more information visit: www.nvidia.com ; llvm.org
Unedited press release follows:
NVIDIA Contributes CUDA Compiler to Open Source Community
Widely Used LLVM Compiler’s Support Opens GPU Computing to Broad Range of Programming Languages
SANTA CLARA, CA–(May 9, 2012) – NVIDIA today announced that LLVM, one of the industry’s most popular open source compilers, now supports NVIDIA GPUs, dramatically expanding the range of researchers, independent software vendors (ISVs) and programming languages that can take advantage of the benefits of GPU acceleration.
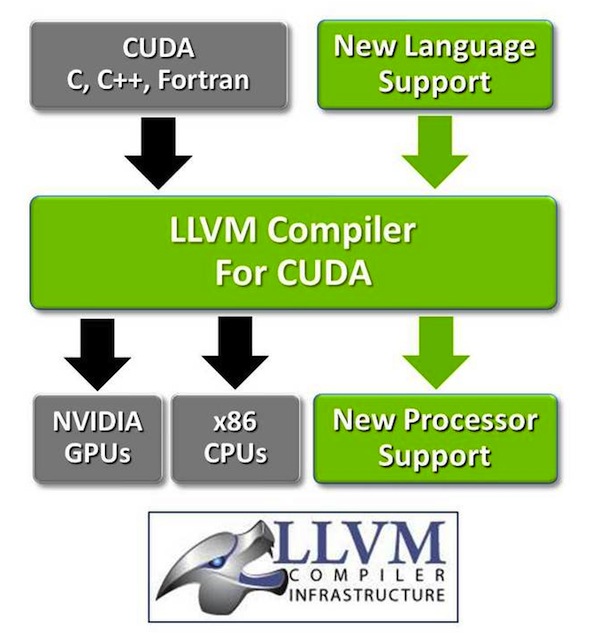
LLVM is a widely used open source compiler infrastructure, with a modular design that makes it easy to add support for programming languages and processor architectures. The CUDA® compiler provides C, C++ and Fortran support for accelerating application using the massively parallel NVIDIA® GPUs. NVIDIA has worked with LLVM developers to provide the CUDA compiler source code changes to the LLVM core and parallel thread execution backend. As a result, programmers can develop applications for GPU accelerators using a broader selection of programming languages, making GPU computing more accessible and pervasive than ever before.
LLVM supports a wide range of programming languages and front ends, including C/C++, Objective-C, Fortran, Ada, Haskell, Java bytecode, Python, Ruby, ActionScript, GLSL and Rust. It is also the compiler infrastructure NVIDIA uses for its CUDA C/C++ architecture, and it has been widely adopted by leading companies such as Apple, AMD and Adobe.
“Double Negative has ported their fluid dynamics solver over to use their domain-specific language, Jet, which is based on LLVM,” said Dan Bailey, researcher at Double Negative and contributor to the LLVM project. “In addition to the existing architectures supported, the new open-source LLVM compiler from NVIDIA has allowed them to effortlessly compile highly optimized code for NVIDIA GPU architectures to massively speed up the computation of simulations used in film visual effects.”
“MathWorks uses elements of the LLVM toolchain to add GPU support to the MATLAB language,” said Silvina Grad-Freilich, senior manager, parallel computing marketing, MathWorks. “The GPU support with the open source LLVM compiler is valuable for the technical community we serve.”
“The code we provided to LLVM is based on proven, mainstream CUDA products, giving programmers the assurance of reliability and full compatibility with the hundreds of millions of NVIDIA GPUs installed in PCs and servers today,” said Ian Buck general manager of GPU computing software at NVIDIA. “This is truly a game-changing milestone for GPU computing, giving researchers and programmers an incredible amount of flexibility and choice in programming languages and hardware architectures for their next-generation applications.”
To download the latest version of the LLVM compiler with NVIDIA GPU support, visit the LLVM site.
To learn more about GPU computing, visit the NVIDIA website. To learn more about CUDA or download the latest version, visit the CUDA website. More NVIDIA news, company and product information, videos, images and other information is available at the NVIDIA newsroom.
About NVIDIA
NVIDIA (NASDAQ: NVDA) awakened the world to computer graphics when it invented the GPU in 1999. Today, its processors power a broad range of products from smartphones to supercomputers. NVIDIA’s mobile processors are used in cell phones, tablets and auto infotainment systems. PC gamers rely on GPUs to enjoy spectacularly immersive worlds. Professionals use them to create 3D graphics and visual effects in movies and to design everything from golf clubs to jumbo jets. And researchers utilize GPUs to advance the frontiers of science with high performance computing. The company has more than 4,500 patents issued, allowed or filed, including ones covering ideas essential to modern computing. For more information, see www.nvidia.com.